
Birth Statistics
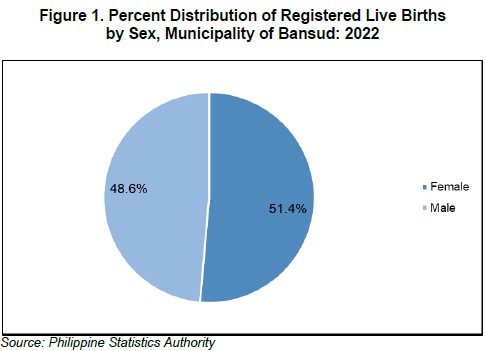
The Municipality of Bansud was able to register 109 births in 2022, equivalent to a decline of 15.5 percent compared to registered births in 2021 with 129 births. Moreover, more females (56 births or 51.4 percent share) were born than males (53 births or 48.6 percent share), resulting in a sex ratio at birth of 95 males per 100 females.
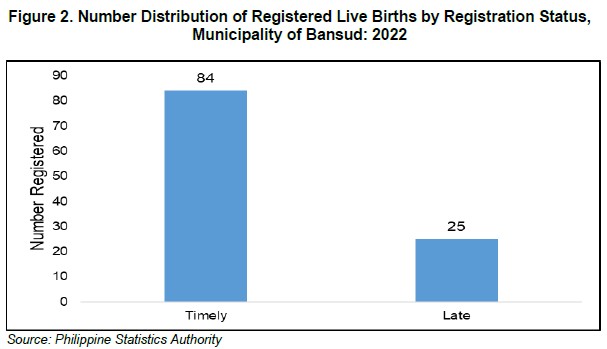
Out of the 109 registered births, 84 births or 77.0 percent were timely registered, of this, 44 births were females (52.3 percent) and 40 births were males (47.6 percent). Conversely, a total of 25 births or 22.9 percent were late registered, 12 births (48.0 percent) were females while 13 births (52.0 percent) were males.
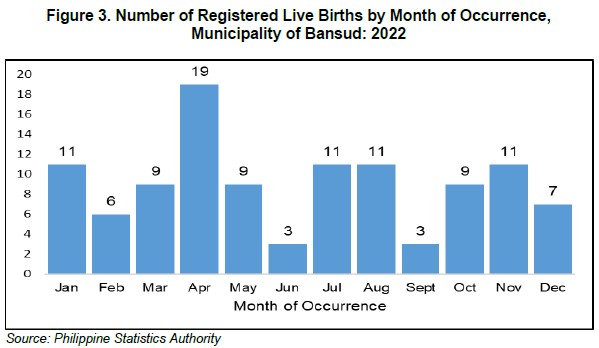
The month of April had the greatest number of registered births with 19 births in all, or 17.4 percent of all births. The months of January, July, August, and November (10.1 percent) came next. June and September, on the other hand, had the lowest percentage of births with both three births. (Figure 3)
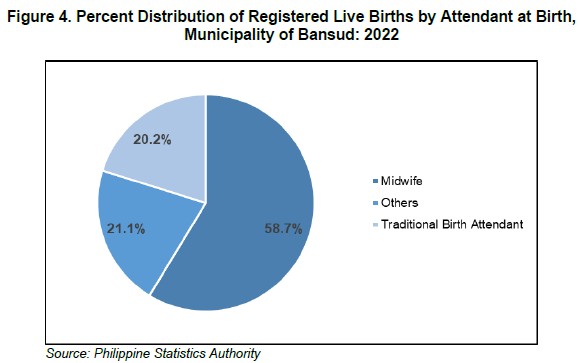
Of the total number of births in Municipality of Bansud, 58.7 percent were attended by midwives and 21.1 percent of births were assisted by someone other than health professionals such as physician and nurse. On the other hand, 20.2 percent were delivered by hilot/traditional birth attendant.
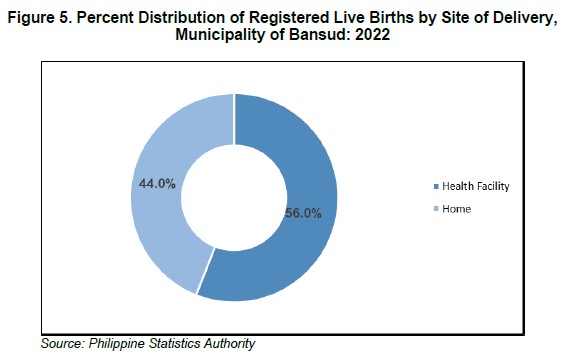
There is a higher percentage of births with 56.0 percent, than those that took place in a hospital, occurred at home. A health institution, such as a hospital, birthing clinic, lying-in, outpatient care center, specialized care center, or the like, was used to deliver just 44.0 percent of newborns.
Mothers between the ages of 25 and 29 accounted for 30 births or 27.5 percent of all births registered in the Municipality of Bansud. Furthermore, 28 births in the town, or 22.9 percent of all births, were from the ages of 20-24 years old.

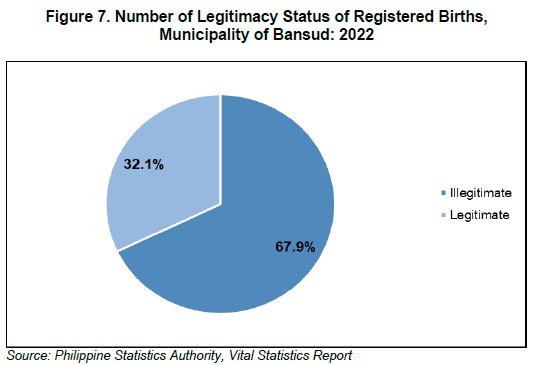
Most registered births were illegitimate children with 74 births or 67.9 percent of the total births in Municipality of Bansud. On the other hand, legitimate children have a fewer total number with 35 births or 32.1 percent of total births registered.
Marriage Statistics
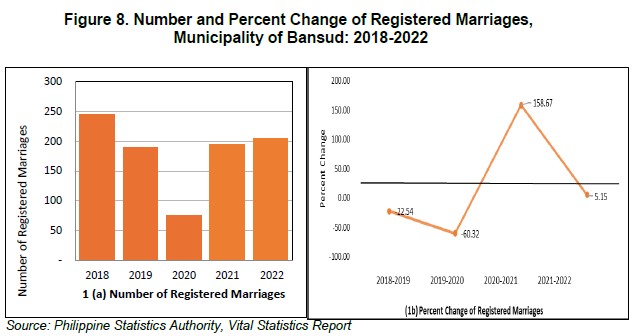
In 2022, a total of 204 marriages were registered, an increase of 5.1 percent from the total registered marriages of 194 in 2021. Comparing with the number before the pandemic, an increase of 7.9 percent was observed from 2019 to 2022.
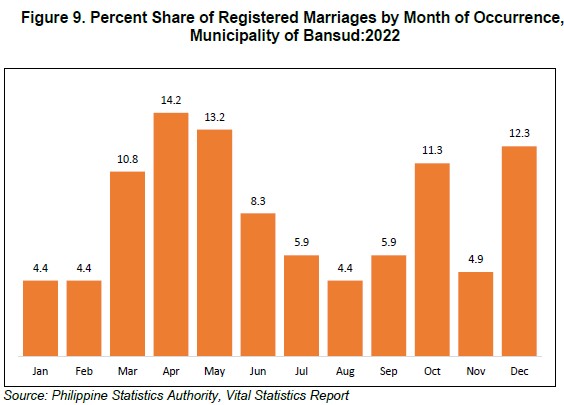
The month April recorded the highest number of registered marriages with 29 marriages or 14.2 percent share of the total marriages in Municipality of Bansud. The months of May ranked second with 27 marriages or 13.2 percent share, followed by the month of December with 25 marriages or 12.3 percent share. On the other hand, the months of January, February and August had the least number of registered marriages with 9 marriages, each, or 4.4 percent share, each. (Figure 9)
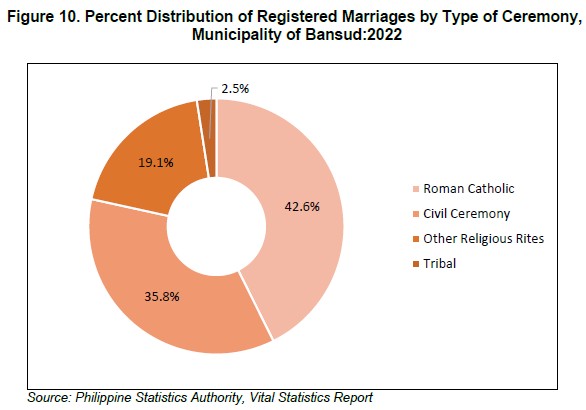
Of the total registered marriages in 2022, 87 marriages or 42.9 percent were officiated in Roman Catholic Churches. About 73 marriages or 36.0 percent were contracted through civil ceremony, while 39 marriages or 19.1 percent were performed in other religious rites. Marriages solemnized in Tribal traditions accounted for 5 marriages or 2.5 percent of the total registered marriage. (Figure 10)
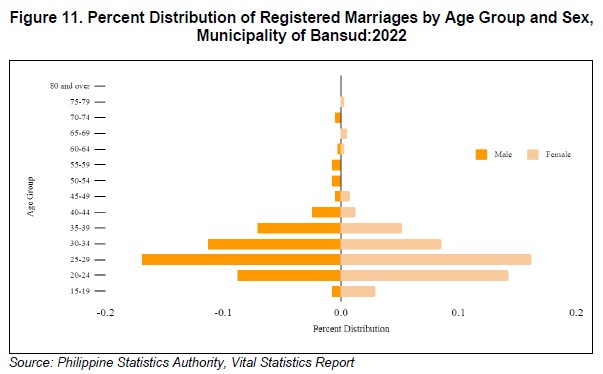
The majority of couples in Municipality of Bansud married between ages 25-29 years. About two in ten men (69 marriages or 16.9 percent) married at these ages, and about the same proportion was observed for women (66 marriages or 16.2 percent).
Additionally, women tend to marry at a younger age than men. Among the total marriages recorded, 12 marriages or 5.8 percent of adolescent females are married before the age of 20, compared to just 3 or 1.4 percent of adolescent males in the same age group.
Death Statistics
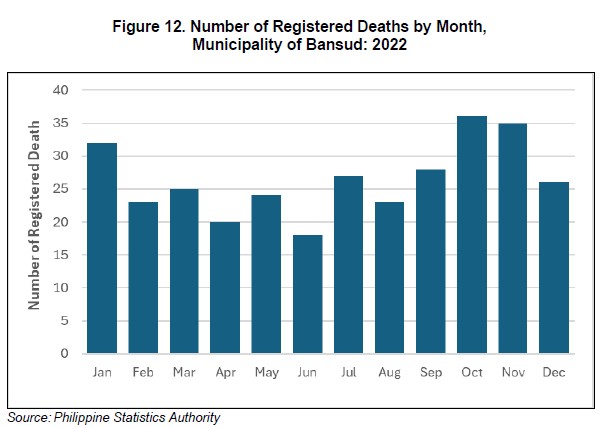
The municipality of Bansud was able to register 317 deaths for the year 2022, translated to an average of 26 deaths per month. Month of October had the highest registration of deaths in 2022 with 36 deaths, followed by the month of November with 35 deaths, then followed by the month of January with 32 registered deaths. Month of June had the least number of registered deaths with only 18 deaths. (Figure 12)
Of the 317 deaths in the municipality of Bansud in 2022, there were 171 male deaths (53.9 percent) and 146 female deaths (46.1 percent).
The top three causes of death in the municipality of Bansud from January to December 2022 were Pneumonia, organism unspecified, Acute myocardial infarction, and Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Pneumonia, organism unspecified, the top leading cause of death in Bansud, managed to take 44 lives or 13.9 percent share of the total deaths in the municipality. On the other hand, Acute myocardial infarction came in second with 35 deaths or 11.0 percent share of all the total deaths in the municipality. Further, Type 2 diabetes mellitus was the third leading cause, which accounted for 24 deaths or 7.6 percent share of all the total deaths in the municipality.
Further, Acute myocardial infarction, is the leading cause of deaths in males, registering 20 deaths or 11.7 percent share of male deaths. Followed by Pneumonia, organisms are unspecified with 12 deaths, and Type 2 diabetes mellitus with11 deaths.
Additionally, Pneumonia, organism unspecified, also is the leading cause of deaths in females, recording 32 deaths or 21.9 percent share of female deaths. Followed by Acute myocardial infarction with 15 deaths, and Type 2 diabetes mellitus with 13 deaths.
Infant deaths are deaths that occur before reaching age one. In the municipality of Bansud, fourteen infant deaths occurred, of which eleven were males and three were females.
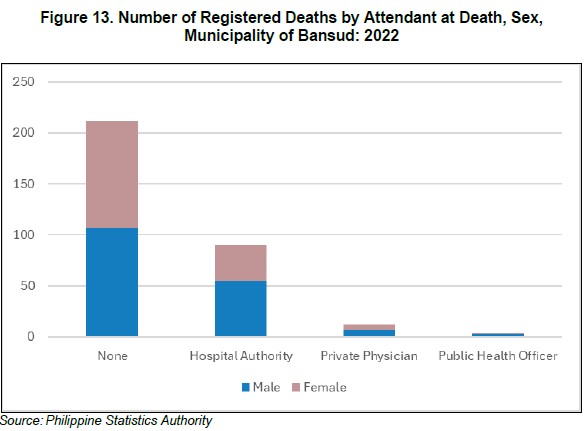
Out of the 317 registered deaths in the municipality, 211 deaths or 66.6 percent were not attended by any of the private physician or public health officer or hospital authority. Of the 211 deceased individuals with no attendant at death, 106 were males and 105 were females.
Moreover, a total of 90 registered deaths were attended by hospital authorities. Of this, 55 were male deaths and 35 were female deaths, respectively.
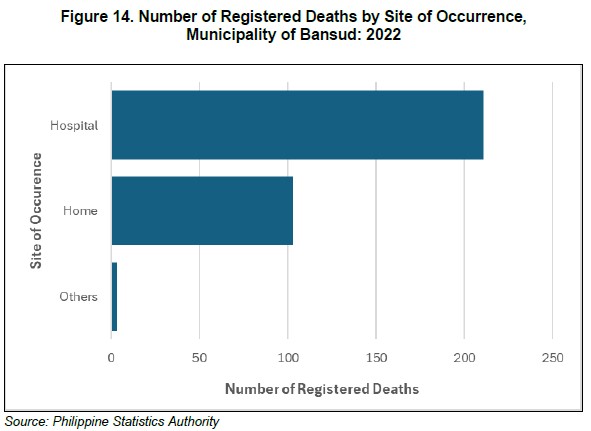
In the municipality of Bansud, 211 registered deaths or 66.6 percent occurred at home, from these, 106 deaths were males (50.2 percent) and 105 deaths were females (49.8 percent). Moreover, there were 103 deaths or 32.5 percent occurred at the hospitals, wherein 63 deaths were males (61.2 percent) and 40 deaths were females (38.8 percent). (Figure 14)
(SGD) CHARLYN ROMERO-CANTOS, PhD
(Chief Administrative Officer)
Officer-in-Charge
Oriental Mindoro Provincial Statistical Office
TECHNICAL NOTES ON VITAL STATISTICS
INTRODUCTION
Vital statistics are derived from information obtained at the time when the occurrences of vital events and their characteristics are inscribed in a civil register.
Vital acts and events are the births, deaths, fetal deaths, marriages, and all such events that have something to do with an individual's entrance and departure from life together with the changes in civil status that may occur to a person during his lifetime. Recording of these events in the civil register is known as vital or civil registration and the resulting documents are called vital records.
STRUCTURE OF VITAL STATISTICS SYSTEM
The production of vital statistics comprised of a system of operations in which the registration of vital events is an important component. The system begins with the registration followed by the processing and controlling of vital records and ends with the compilation and analysis of vital statistics.
Under Commonwealth Act (CA) 591, the Bureau of Census (now Philippine Statistics Authority) is mandated to generate general purpose statistics and to carry out and administer Act No. 3753.
Under the same law, the head of the PSA is also the Civil Registrar General (CRG) who directs and supervises the local civil registration activities in the country. The CRG in this regard is empowered to prepare and issue implementing rules and regulations on civil registration and to prepare and order printed the necessary forms for proper compliance.
The set-up of vital statistics system involves different entities and cuts across different departments and personalities.
For the registration of vital events, the Local Civil Registry Offices (LCROs), which are the registration units in the country and headed by the City/Municipal Civil Registrars (C/MCRs), are under the Local Government Units (LGUs). The hospitals, clinics, rural health units and similar institutions including barangay secretaries, practicing physicians, midwives, nurses, traditional midwives, solemnizing officers from various religious sects and denomination are required to assist in the reporting of vital events for registration at the LCROs. The concerned parents, next of kin, contracting parties, a witness or the person who has full knowledge of the occurrence of the event are also required to report the event, in default of the first mentioned set of informants.
The processing and controlling of vital documents are done at the LCROs and at the PSA Provincial and Central Offices.
The compilation and analysis of vital statistics is taken cared of by the PSA Central Office under the Vital Statistics Division of the Civil Registration and Central Support Office.
THE REGISTRATION METHOD
As mandated in Act 3753, all vital events that marked the entry and departure of a person in his lifetime and the changes in his/her civil status shall be registered. The registration method is defined as the continuous, permanents and compulsory recording of the occurrences and characteristics of vital events, primarily for their value as legal documents and secondary for their usefulness as a source of statistics.
Place where to register the event
As a general rule, the place of registration is the LCRO of the city of municipality where the vital events occur.
Out of town reporting of vital event occurs when the documents presented to the civil registrar of LCRO, which is not the place of occurrence, not for registration but to be forwarded to the civil registrar of LCRO where the event occurred and where it should be registered.
Forms to use
The civil register consists of certificates and the registry book. It also includes the actual copies of the registrable court decisions and the legal instruments concerning the civil status of persons. The certificates are loose-leaf forms in a set of four copies except for the Certificate of Foundling which is in a set of three.
Person who will report the event
The informant is the one who reports the event for registration and who gives information to be recorded in the civil register.
For death occurrences, the report shall be made by the hospital or clinic administrator if the person dies in the hospital or clinic, or by attending physician or by the nearest relative or by any interested party who has knowledge of the occurrence of death. In all cases, the report shall be submitted to the Local Health Officer (LHO) who shall direct and order the C/MCR to enter the death in the civil register.
Period when to report the event
Death or fetal death shall be reported to LHO within forty eight (48) hours from the time of death and the LHO shall direct or cause the registration to the C/MCR not later than thirty (30) days from date of death.
Any report made to the LCROs beyond the reglementary period are considered late and can be entered only in the civil register after the informant complies with the requirements for delayed registration.
Operative Act of Registration
The C/MCR sees to it that appropriate form it used; form is properly and completely filled-up; and proper attachments are submitted. In case, the entries are found incomplete, the C/MCR has to require the person concerned to fill up the document completely or to correct the entries.
When the document is accepted for registration, the date of receipt is recorded in the space provided and the documents received for the day are entered immediately in the appropriate civil registry book, assigning therein the corresponding registry number. After registration entry/entries found erroneous can only be corrected through RA 9048, except sex, nationality, age and status which require court approval.
Distribution of registered documents
Upon registration, the C/MCR distributes the copies accordingly: the first copy to the informant; the second copy to the CRG; the third copy shall be retained by the LCRO; and the fourth copy to the attendant or solemnizing officer, as the case may be. The CRG copy is the source of vital statistics published in this report.
DEFINITION OF TERMS AND CONCEPTS
Significant terminologist and descriptions in the foregoing highlights and tables are defined below. Included are some items found in the certificates and summary measure used in describing the facts of events.
Death refers to the permanent disappearance of all evidence of life at any time after live birth has taken place (postnatal cessation of vital function without capability of resuscitation).
Crude Death Rate (CDR) refers to the number of deaths per 1,000 mid-year population.
Daily Average refers to the arithmetic mean of birth, death or marriage occurrences per day.
Daily Index is the increase/decrease from the overall daily average of event occurrences.
Usual Residence refers to the place where the person habitually or permanently resides.
Place of Occurrence refers to the place where the vital event took place.

