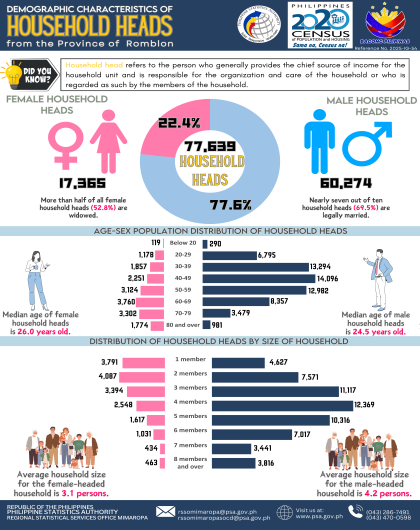
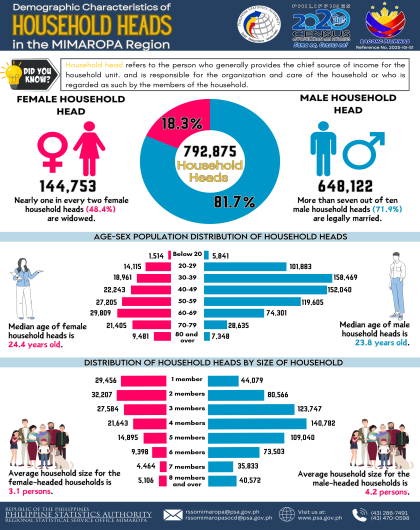
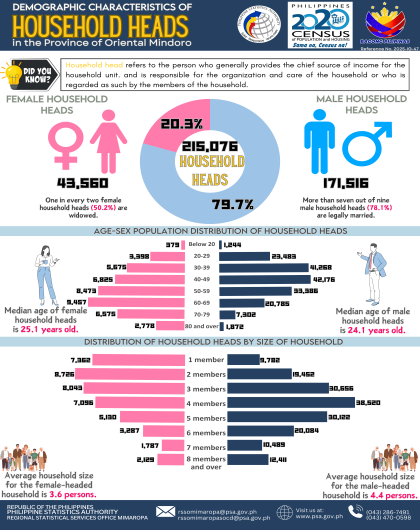
Institutional population decreases by 584
As of 01 May 2020, the institutional population reached 16,271 persons, or 0.50 percent of the region’s total population of 3,228,558 persons. This figure is 584 persons or 3.46 percent lower than the 16,855 institutional population posted in 2015. The number of institutional living quarters (ILQs) rose by 840 or 83.25 percent from 1,009 in 2015 to 1,849 in 2020. (Figure 1)
Nearly two in every three ILQs are of residential type
Hotels, motels, lodging houses, and dormitories consistently comprised the largest number of ILQs in the country in 2015 and 2020. This type of ILQ accounted for 1,190 (64.36 percent) of the total 1,849 ILQs in 2020. Convents, nunneries, seminaries, and boarding schools came in next with 194 ILQs or 10.49 percent, followed by military camps and stations with 159 ILQs or 8.60 percent. (Figure 2 and Table A)
Nearly half of the institutional population reside in corrective and penal institutions
Among 16,271 institutional population in the MIMAROPA Region, there were 7,752 persons (47.64 percent) resided in corrective and penal institutions. Residents in hotels, motels, lodging houses, and dormitories was next with 4,056 persons (24.93 percent), followed by those residing in military camps and stations with 1,517 persons (9.32 percent). These were also the top three most numerous institutional population in 2015. (Figure 3 and Table A)
Eight in every nine ILQ residents are male
In 2020, eight in every nine persons residing in ILQs or 86.77 percent were males while 13.23 percent were females. This resulted in a sex ratio of 656 males per 100 females.
Majority or 91.20 percent of the institutional population belong to the age group of 15 to 59 years. The rest of the institutional population were aged 0 to 14 years (2.33 percent) and 60 years and over (6.47 percent). More males were seen living in ILQs that belonged to the age group 15 to 59 years and 60 years and over with a sex ratio of 713 males per 100 females, and 680 males per 100 females, respectively. (Figure 4 and Table B)
Meanwhile, females outnumbered males among institutional population whose age is 0 to 14 years old, as the sex ratio for this age group was 97 males for every 100 females.
In 2020, males outnumbered females in all types of ILQs, except in hospital and nurses’ home, where females accounted for 51.37 percent while males comprised 48.63 percent, or a sex ratio of 95 males for every 100 females. (Table 1 and Table A)
Half of the institutional population are never married
One in every two or 50.01 percent of the 16,057 ILQ residents aged 10 years and over, was never married while 38.80 percent was married. Males outnumbered females on these marital status such that males got a share of 81.64 percent among never married institutional population and 93.26 percent share among married institutional population. (Figure 5 and Table D)
The rest of the institutional population 10 years old and over was categorized as follows: in common-law/live-in marital arrangement (5.24 percent), widowed (2.40 percent), and divorced/separated/annulled (1.69 percent). In each of these marital statuses, nine out of ten persons residing in ILQs were males; that is, male accounted for the 91.44 percent among those with common-law/live-in marital arrangement, 87.53 percent of widowed institutional population and 89.71 percent of institutional population who were divorced, separated or annulled.
TECHNICAL NOTES
I. Introduction
The Philippine Statistics Authority conducted the 2020 Census of Population and Housing (2020 CPH) in September 2020, with 01 May 2020 as reference date.
The 2020 CPH was the 15th census of population and 7th census of housing that was undertaken in the Philippines since the first census in 1903. It was designed to take inventory of the total population and housing units in the country and collect information about their characteristics.
The Philippine Standard Geographic Codes as of April 2022 was used for the disaggregation of geographic levels of the 2020 CPH.
II. Definition of Terms and Concepts
Most of the operational definitions and concepts adopted in 2020 CPH have also been used in past censuses of population. The use of the same operational definitions of terms and concepts and adherence to national and international standards in population censuses aimed at ensuring the comparability of census results across different census years and census data of other countries. Enumerators of the 2020 CPH were instructed to adhere strictly to these operational definitions.
All persons were enumerated in their usual place of residence, which refers to the geographic place (street, sitio/purok, barangay, city/municipality or province) where the person usually resides. As a rule, a person’s usual place of residence is the place where he/she sleeps most of the time. Hence, it may be the same as or different from the place where he/she was found at the time of the census.
Institutional living quarter (ILQ) is a structurally separate and independent place of abode intended for habitation by large groups of individuals (10 or more). Such a quarter usually has certain common facilities such as a kitchen and dining room, toilet and bath, and lounging area which are shared by the occupants. Occupants of an ILQ are usually subject to a common authority or management or are bound by either a common public objective or a common personal interest.
In the 2020 CPH, only the following ILQs which were in operation at the time of the census were listed:
Hotel, motel, inn, dormitory, pension house, and other lodging house which provide lodging on a fee basis,
Hospital, sanitarium, and rehabilitation center,
Orphanage and home for the aged,
Seminary, convent, boarding school, and other religious training centers,
Corrective and penal institution,
Military camp and barrack,
Logging, mining, and construction/public work camp, and
Oceangoing and interisland/coastal vessel at port.
Institutional population comprises of persons who are found living in ILQs. They may have their own families or households elsewhere but at the time of the census, they are committed or confined in ILQ, wherein they are usually subject to a common authority or management, or bound by either a common public objective or a common personal interest.
The following persons are to be considered as members of the institutional population:
Permanent lodger in a boarding house,
Dormitory resident who does not usually go home to his/her household at least once a week,
Hotel resident who has stayed in the hotel for more than six (6) months at the time of the census,
Boarders in a residential house provided that their number is 10 or more. If the number of boarders in a housing unit is less than 10, they will be considered as members of a regular household, not of the ILQ.
Patient in a hospital who is confined for more than six (6) months,
Patient confined in a mental hospital and drug rehabilitation center, regardless of the length of his/her confinement,
Ward in an orphanage, home for the aged, and other welfare institutions,
Prisoner in a corrective and penal institution,
Seminarian, nun, monk, and postulant,
Soldier in a military camp that stayed for more than six (6) months, and
Worker in a mining and similar camp that stayed more than six (6) months.
The following persons are not considered as members of the institutional population and should be included in the households to which they belong:
Military official/enlisted man or draftee and members of his/her household who has a housing unit within a military installation or camp,
Manager and members of his/her household of dormitory, hotel, hospital, and others, who occupies and regularly uses as his/her place of abode a living quarter in the institution that he/she manages,
Priest, Pastor or Imam who, together with his/her relatives and/or household help, occupies and regularly uses as his/her place of abode a living quarter in the church or seminary.
Sex is the biological and physiological reality of being a male or female.
Age refers to the interval of time between the person’s date of birth and his/her last birthday prior to the census reference date. It is expressed in completed years or whole number.
Age-sex structure is the composition of a population as determined by the number or proportion of males and females in each age category. The age-sex structure of a population is the cumulative result of past trends in fertility, mortality, and migration. Information on age-sex composition is essential for the description and analysis of many other types of demographic data.
Population pyramid is a bar chart, arranged vertically, that shows the distribution of a population by age and sex. By convention, the younger ages are at the bottom, with males on the left and females on the right.
Sex ratio is the number of males per one hundred females in a population.
Marital status refers to the personal status of each individual with reference to the marriage laws or customs of the country. It is the same as civil status, the term usually used in official and private records, documents, transactions, and others, in the country. For the 2020 CPH, the person’s marital status was as of the date of the visit. The following were the categories used for marital status:
Single – person who has never been married.
Married – person married in a religious, civil ceremony or tribal rite, either living with his/her spouse at the time of visit or temporarily living apart because his/her spouse is employed elsewhere (as in the case of a person whose spouse is an overseas worker or one who works with the Armed Forces and residing somewhere else).
Widowed – married person whose spouse died and who has not married up to the time of visit.
Divorced/separated – person who is permanently separated from his/her spouse, legally or through mutual consent. This is also applicable to a person whose marriage with another person has been annulled or dissolved and can, therefore, remarry.
Common-law / live-in – person cohabiting or living consensually with another person as husband and wife without the benefit of a legal marriage.
Unknown – person whose marital status is unknown to the respondent, or whose marital status is being concealed by the respondent/person himself/herself.
Highest grade/year completed refers to the highest grade or year completed in school, college, or university as of May 1, 2020. This may be any one of the specific grades or years in elementary, high school, K to 12 Program, and college. It may also be special needs education program, second-chance education program, or any of the post-secondary, short-cycle tertiary, college, and post baccalaureate courses. A person’s highest grade/year completed was categorized as follows:
No grade completed (did not undergo formal schooling),
Preschool,
Inclusive/Special Needs Education (SPED) Program,
Elementary,
High school,
Post-secondary,
Short-cycle tertiary,
Baccalaureate/College undergraduate,
Baccalaureate/College graduate,
Post baccalaureate (Master’s and doctoral degree students and graduates both fell under this category; also included here were students in law or medical school, as well as students who were still working on their master’s degree, taking doctoral studies, and those who had already completed their master’s or doctoral degree).